How to Use SEO on Your Website
You don't have to pay a firm thousands of dollars a month to apply the principles of Search Engine Optimization (SEO) to your site. All it takes is a little extra effort on the part of content creators and page template designers to increase your rank in search engine results.
Overview
The primary metric search engines use is the number of other high-quality sites that link to your content. The overall process for each piece of content looks something like this:
- Post interesting content
- Build your page in such a way that search engines can 'read' your content
- Make your results appear attractive in search engine results
- Use legitimate marketing means to spread word about the content
After that, it's up to other sites to link to you to help raise your relevance (and thus your rank).
How to Build Your Content
- Identify content keywords
- Write meaningful page and section titles using those keywords
- Add the title of the page to the URL
- Use meta tags and rich content snippets to improve appearance in search engine results
- Make sure your pages load fast & are error-free
Identify Content Keywords
Since users discovering your site through search are doing so by searching for words or phrases related to your content, the first step to optimizing your site for search is to think about what words or phrases users are likely to enter into a search engine to get to content you write. For a product page, this may take the form of product names, brand names, nicknames, or key features. For articles, the topic, sections, and key concepts make good keywords.
Write Meaningful Page & Section Titles
Search engines give more weight to the content inside your page's header tags (<h1>, <h2>, <h3>) as these tags are meant to indicate the overall topic of the page as well as define the titles for sections. Using clear and meaningful page and section headers helps search engines to understand the overall concepts your page is covering.
In addition to the fact that search engines place some importance on the content of the <title> tag, this tag also controls the title of the page in search engines:
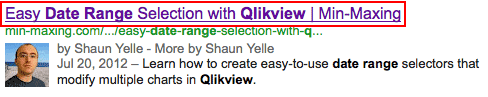
Note: Your content management systems (CMS) may handle the title and top-level header pieces for you when you enter the title of your page into the CMS.
Add Page Title to URL
Search engines give some weight to the text in the URL of a page as well, so placing the title into the URL as well can help rankings. In addition, users can look at a raw link and get an idea of what is behind it, which aids in overall understanding of what content hides behind it.
Note: Your CMS may also handle putting the title in the URL for you when you enter the title of your page into the CMS.
Use Meta Tags and Rich Content Snippets
By using the meta description tag(<meta name="description" content="Page description here">), you can tell search engines what you want the description of the page to be:
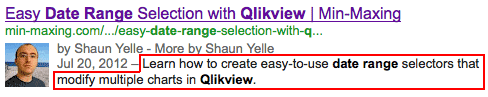
Keep in mind, however, that this doesn't guarantee that a search engine will use your description. If, for example, you searched for terms that appeared to be more relevant in the content of the page, search engines would use a snippet from the content instead.
Depending on the search engine, you can use additional markup to highlight additional information such as the author of an article and the date it was published:
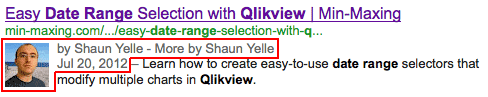
Google has an article on how to show author information in Google search results.
Make sure your pages load fast & are error-free
To a minor degree, the time it takes for your pages to load can affect your page rank. While it only directly affects very slow sites, there is evidence that indicates users will spend less time on your site if it is slow. In addition, if your page has any errors, it can inhibit a search engine's ability to parse all of the content.
What about images?
The only clue search engines have for what your images contain is the alt attribute on the <img> tag. Make sure you desscribe what is inside the image using the alt text to make sure the image content is properly understood by search engines.
What about social media?
As of now, there's no huge argument for Facebook and Twitter affecting your page rank outside of marketing your content in hopes that people will link it elsewhere. Some search engines have begun looking at social networks for hints about popular content, but they only use it in limited situations. Search Engine Land has some more details on what social signals are used by search engines.
Bad SEO Practices
There are some methods people and SEO companies have attempted to use to 'game' search engine algorithms. In general, it's always a bad idea to attempt such methods as they are actively combated by search engine providers and they will penalize you if they detect that you use them.
- Loading content via JavaScript after page load
- Serving content to search engines that is different from what users see
- Paid links & link spam
- Duplicating Content
Loading content via JavaScript after page load
Search engine bots are like other bots in that they can parse the content that your page generates, but nothing that you inject after page load via JavaScript. Any such content will not be archived by a search engine.
Serving Different Content
Some people have attempted to increase the size of their page rank by stuffing keywords or extra content on a page such that normal users will not see them but a search engine would see them. Search engines are becoming progressively more able to detect this kind of content stuffing and will lower your rank if they detect this behavior.
Paid links & link spam
Since rank is dependent on how many sites link to you, some people have attempted to increase their rank by either spamming their links on other sites or by paying other sites to link to them. Just like with content hiding, search engines can detect spam patterns and will lower your rank accordingly. In addition, if there are links to your site from known 'bad neighborhoods' on the internet (link farms, for example), you will be penalized as a result.
Duplicating Content
Simply copying content from another site will not help increase your rank. Search engines look for duplicate content and penalize copycat pages. Google is even taking valid copyright claims into account in their algorithms: any site that habitually violates copyright laws may be penalized as a result.
Conclusion
Overall, once you lock in a page template that is friendly to search engines, the only on-going tasks you have is to make sure each new piece of content has appropriate keywords used for titles, headers, and throughout the content to help aid discovery via search. From there, keep writing interesting content!

If you liked this article, you may want to: